Disney Princesses At Their Current Ages
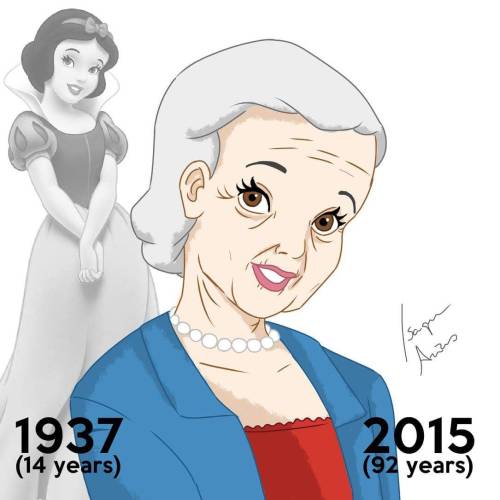
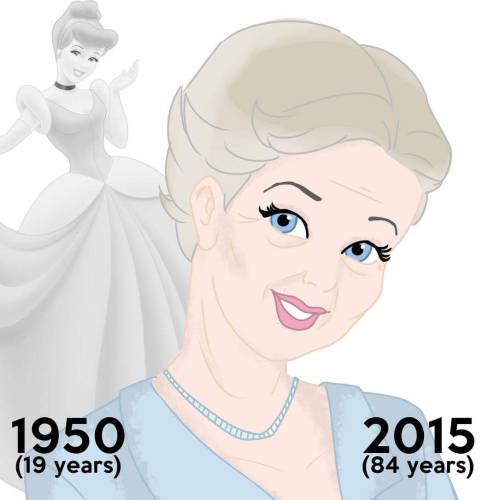
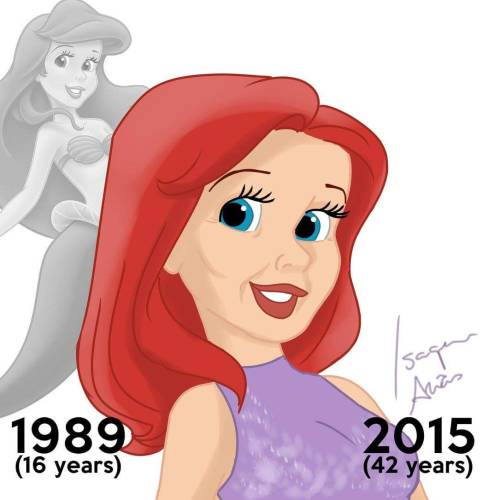
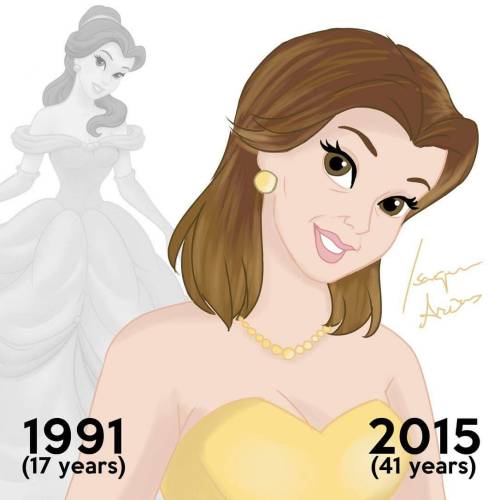
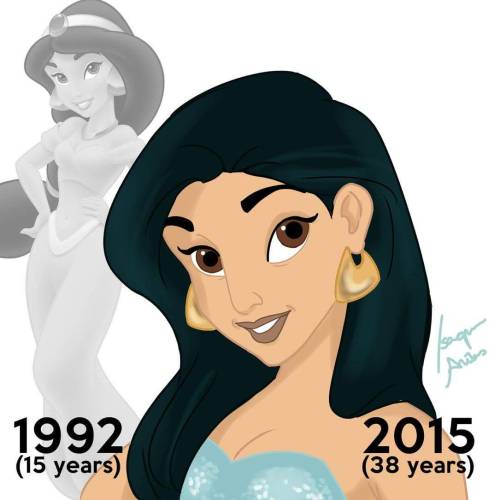
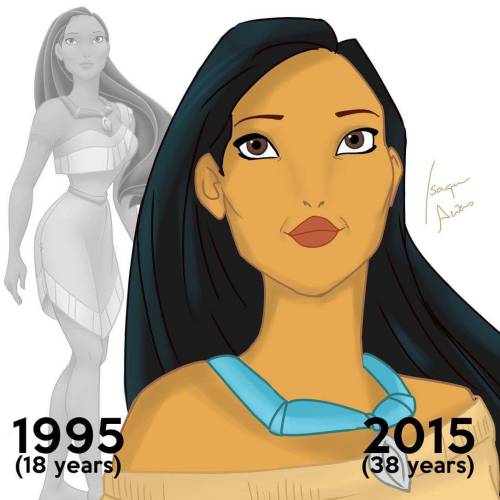
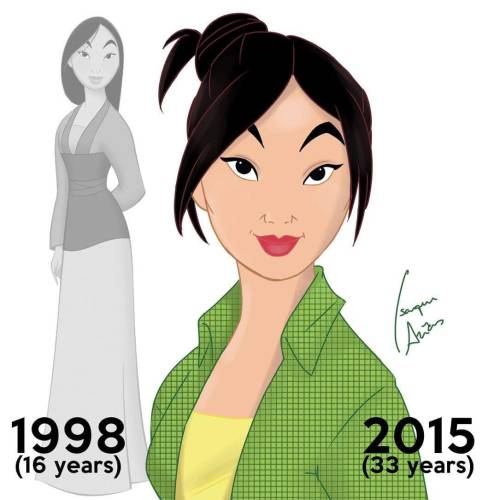
Disney Princesses at their Current Ages
More Posts from Feralpaules and Others
Writing from Scratch #2:
What is a Plot?
Different people mean different things when they use the word “plot,” and they are all correct, if not as descriptive as they could be.
Some people mean a story structure, like the 3-Act Structure; some people mean a plot archetype, like an underdog sports plot or a heist plot; some people mean the negative to positive or positive to negative trajectory of the main character, like Rags to Riches; and some people mean “to plot” as in “to outline.”
Throughout Writing from Scratch, when I say “plot,” I’ll be referring to the definition I’ve already hinted at: a plot is a problem and its solution. Plots of this nature can be very long if the solution takes a while for the character to arrive at or very short if the solution is solved without much trouble. In a story with multiple plots of this type, the plot that has its problem first introduced and last solved is what I will call the Long Plot.
Plot-Problems
There are four umbrella types that plots of this kind fall under – all based on the type of problem the plot has. And these are called the MICE* plot-problems.
Milieu
Inquiry
Character
Event
Over the next few posts, I will be diving into each in turn.
*The MICE Quotient was developed by Orson Scott Card, but I do deviate in my approach from the way Scott Card developed it and from the way most other writers teach it.
Plot-Solutions
A plot’s solution comes through what are referred to as the Try-Fail Cycles. The character is introduced to the problem, tries to solve it, and succeeds or fails. Most plots are solved after the character has failed to solve it at least once.
The Try-Fail typically goes in one of two directions: “Yes, but…” or “No, and…”
The “Yes, but” failure follows the character trying something with “yes, that technically worked, but now a new aspect of the same problem has been revealed.”
Obi-Wan and Luke hire Han and Chewie to take them and the droids to Alderaan. Yes, Han and Chewie get them to where Alderaan should be in orbit, but the Death Star got there first and blew the planet up.
The “No, and” failure follows the character trying something with “no, that didn’t work, and now the situation has worsened as a result.”
Harry and Ron run off to warn Hermione that there is a troll loose in the castle and get her to come back with them to the Gryffindor Common Room. No, they do not get a chance to warn Hermione about the troll, and they have locked the troll in the girls’ bathroom with Hermione.
“No, and” can also be a final – fatal – plot-solution, but this is not usually very satisfying. The ultimate plot solutions are typically either “Yes, and…” or “No, but…”
Prompt: Analyze a plot (that is a problem (subject) and solution with try-fail cycles (predicate)) in a favorite book, movie, or TV episode. I'll be posting my analysis this Sunday; if you're from the future, check it out here!
If you want to read more, you can check out my over 80 WfS posts on my website theferalcollection.com
Writing from Scratch #9: Complex Plots, Part 2
Writing from Scratch #9: Complex Plots, Part 2. Writing from Scratch is a weekly blog series that takes writing back to the basics. #writing #writingadvice
Writing from Scratch is a weekly blog series that takes writing back to the basics. Each week we’ll build on what we’ve learned before to craft our stories.
Go to index. Go to first post. Go to previous post.
Complex Plots, Part 2: Modifying Plots
The second way we’ll try complicating a plot is through plot modifiers. This happens when a try-fail cycle not only furthers the solution of…
View On WordPress
Writing from Scratch #7: The Event Plot
The Event Plot
The problem of an Event plot is a disruption to the status quo. The solution comes either from setting everything right again or adapting to the change. The Event plot is probably what most people think of when they think “what is a plot?” Any story that deals with a life-changing or world-changing event is an Event.
The first plot I analyzed, from The Expanse television series, is an Event plot. Let’s look at another: The Princess Diaries. As we did with Lord of the Rings, we’ll look at the movie rather than books because more people will be familiar with the movie (which is a damn shame).
The Event: Mia Thermopolis’s grandmother tells Mia that she is the princess of small European kingdom Genovia, and she must take the throne.
Read More on WordPress
Auditions and Plays and Queries, Oh My!
Life-changing audition, a friend's play, and writing those queries. #actorslife #writerslife
Been gearing up for a big, potentially life-changing, audition. It just doesn’t seem real yet. I feel like I’m drifting along in a dream state, and this is some far off thing when it really isn’t. I mean, I’m prepared. I just feel like until I’m actually in the room, I’m not going to accept that this could be happening to me. And maybe I’m just protecting myself from the very real…
View On WordPress
On Liking Stuff (or not)
So, back when Ancillary Justice was essentially sweeping that year’s SF awards, there was some talk from certain quarters about it not really being all that, people only claimed to like it because Politics and SJWs and PC points and Affirmative Action and nobody was really reading the book and if they were they didn’t really enjoy it, they just claimed they did so they could seem cool and woke.
My feelings were so hurt that I wept bitter, miserable tears every time I drove to the bank with my royalty checks. I mean, those people must be right, it’s totally typical for non-fans who don’t actually like a book to write fanfic or draw fan art, totally boringly normal for students to choose to write papers about a book that just isn’t really very good or interesting, and for professors to use that boringly not-very-good book in their courses, and for that book to continue to sell steadily five years after it came out. I totally did not laugh out loud whenever I came across such assertions, because they were absolutely not ridiculous Sour Grape Vineyards tended by folks who, for the most part, hadn’t even read the book.
Now I am sorry–but not surprised–to see some folks making similar assertions about N.K. Jemisin’s historic (and entirely deserved) Hugo Threepeat. Most of them haven’t read the books in question.
But some of them have. Some of them have indeed read the books and not understood why so many people are so excited by them.
Now, Nora doesn’t need me to defend her, and she doesn’t need lessons from me about the best way to dry a tear-soaked award-dusting cloth, or the best brands of chocolate ice cream to fortify yourself for that arduous trip to the bank. Actually, she could probably give me some pointers.
But I have some thoughts about the idea that, because you (generic you) didn’t like a work, that must mean folks who say they did like it are Lying Liars Who Lie to Look Cool.
So, in order to believe this, one has to believe that A) one’s own taste is infallible and objective and thus universally shared and B) people who openly don’t share your taste are characterless sheep who will do anything to seem cool.
But the fact is, one doesn’t like or dislike things without context. We are all of us judging things from our own point of view, not some disembodied perfectly objective nowhere. It’s really easy to assume that our context is The Context–to not even see that there’s a context at all, it’s just How Things Are. But you are always seeing things from the perspective of your experiences, your biases, your expectations of how things work. Those may not match other people’s.
Of course, if you’re in a certain category–if you’re a guy, if you’re White, if you’re straight, if you’re cis–our society is set up to make that invisible, to encourage you in the assumption that the way you see things is objective and right, and not just a product of that very society. Nearly all of the readily available entertainment is catering to you, nearly all of it accepts and reinforces the status quo. If you’ve never questioned that, it can seem utterly baffling that people can claim to enjoy things that you see no value in. You’ll maybe think it makes sense to assume that such people are only pretending to like those things, or only like them for reasons you consider unworthy. It might not ever occur to you that some folks are just reading from a different context–sometimes slightly different, sometimes radically different, but even a small difference can be enough to make a work seem strange or bafflingly flat.
Now, I’m sure that there are people somewhere at some time who have in fact claimed to like a thing they didn’t, just for cool points. People will on occasion do all kinds of ill-advised or bananapants things. But enough of them to show up on every SF award shortlist that year? Enough to vote for a historic, record-breaking three Hugos in a row? Really?
Stop and think about what you’re saying when you say this. Stop and think about who you’re not saying it about.
You might not have the context to see what a writer is doing. When you don’t have the context, so much is invisible. You can only see patterns that match what you already know.*
Of course, you’re not a helpless victim of your context–you can change it, by reading other things and listening to various conversations. Maybe you don’t want to do that work, which, ok? But maybe a lot of other folks have indeed been doing that, and their context, the position they’re reading stories from, has shifted over the last several years. It’s a thing that can happen.
Stop and think–you’ve gotten as far as “everyone must be kind of like me” and stepped over into “therefore they can’t really like what they say they like because I don’t like those things.” Try on “therefore they must really mean it when they say they like something, because I mean it when I say it.” It’s funny, isn’t it, that so many folks step into the one and not the other. Maybe ask yourself why that is.
This also applies to “pretentious” writing. “That writer is only trying to look smart! Readers who say they like it are only trying to look smarter that me, a genuine,honest person, who only likes down-to-earth plain solid storytelling.” Friend, your claims to be a better and more honest person because of your distaste for “pretentious” writing is pretension itself, and says far more about you than the work you criticize this way. You are exactly the sort of snob you decry, and you have just announced this to the world.
Like or don’t like. No worries. It’s not a contest, there’s no moral value attached to liking or not liking a thing. Hell, there are highly-regarded things I dislike, or don’t see the appeal of! There are things I love that lots of other folks don’t like at all. That’s life.
And sure, if you want to, talk about why you do or don’t like a thing. That’s super interesting, and thoughtful criticism is good for art.
But think twice before you sneer at what other folks like, think three times before you declare that no one could really like a thing so it must be political correctness, or pretension, or whatever. Consider the possibility that whatever it is is just not your thing. Consider the possibility that it might be all right if not everything is aimed at you. Consider that you might not actually be the center of the universe, and your opinions and tastes might not be the product of your utterly rational objective view of the world. Consider the possibility that a given work might not have been written just for you, but for a bunch of other people who’ve been waiting for it, maybe for a long time, and that might just possibly be okay.
____ *Kind of like the way some folks insist my Ancillary trilogy is obviously strongly influenced by Iain Banks (who I’d read very little of, and that after AJ was already under way) and very few critics bring up the influence of C.J. Cherryh (definitely there, deliberate, and there are several explicit hat tips to her work in the text). Those folks have read Banks, but they haven’t read Cherryh. They see something that isn’t there, and don’t see what is there, because they don’t have the same reading history I do. It’s interesting to me how many folks assume I must have the same reading history as they do. It’s interesting to me how sure they are of their conclusions.
(Crossposted from https://www.annleckie.com/2018/08/27/on-liking-stuff-or-not/)
Writing from Scratch #3
Flash Fiction: A Simple Plot
The first writing prompts we’re going to tackle will be flash fiction pieces. Flash fiction is a complete story written in under 1,500 words. We’ll be aiming for 250-500 words at first – that is one or two pages double spaced written in Times New Roman 12 pt. font.
The type of flash fiction I’ll encourage you to write will be Eighteen Sentence Stories*, and each of these sentences will have a very specific job.
The first Three sentences will provide the main character, the setting, and the genre (which clues the audience in on what kind of story they are about to read).
The main character should be introduced via an action that reveals their attitude at the start and with one defining job or trait that relates them to the plot. For example, a character may be both a father of three and a pilot. If the problem of the plot will deal with the kidnapping of one of his daughters, then “father” or “father of three” will be the defining job; if the problem of the plot will deal with the starship he’s piloting falling under attack, then “pilot” will be the defining job.
The setting should be introduced via a grounding sensory detail. The lingering scent of cookies left to burn when the parents received the ransom note. Or the pressure of being pinned back into the pilot’s seat under g forces.
The genre should be introduced via something specific and unique to the story. A ransom note is not specific or unique; a ransom note scrawled on the back of a picture that went missing off the fridge the week before is. A space ship is not specific or unique; a living space ship with a giant brain in its core that the pilot must psychically link to via the tentacles that suction onto his temples is.
Read More on WordPress
Writing from Scratch #8
Now that we have gone over the four simple plot-problems (1, 2, 3, 4) and how they are solved through try-fail cycles, we’ll take a look at how to make complex, compound, and compound-complex plots through the same devices as sentence creation.
The first way we’ll try complicating a plot is by making the solution of the first noted plot-problem dependent on the solution of a second plot-problem, which stands in for easy solution prevention. We’re typically going to use dependent plots to strengthen audience satisfaction when the character is finally able to succeed. Or, like in the case-study we’ll look at today, they can be used to draw what appeared to be disparate plots together in longer works.
Read more on WordPress
Quick Plotting Tip: Write Your Story Backwards
If you have a difficult time plotting, try writing or outlining your story backwards—from the end to the beginning. Writers who have a difficult time outlining, plotting, and planning their stories often benefit from this technique. You’ll need a general idea of what your story is about for this to work, and of course you need to know the ending, but you might be amazed how helpful this trick can be.
Why is writing backwards easier? Basically, instead of answering the question “this happened… now what comes next?,” you’ll be answering the question “this happened… so what would come right before that?” which narrows the possibilities for your next move and can help keep your story on track. (Incidentally, it’s also the way Joseph Gordan-Levitt’s character comes out on top in the film The Lookout.)
Writing backwards can also help you more tightly weave together your subplots, themes, and character relationships, and keep you from going too far down any irrelevant rabbit holes.
If you don’t want to write or outline completely backwards, remember that you’re free to jump around! If you’re feeling stuck in your story or novel, jump to the middle or end and write a few scenes. Many writers get stuck because they feel they have to write their story linearly from beginning to end, which results in an overdeveloped (and often irrelevant) beginning and an underdeveloped ending.
So go work on that ending! It’s much more likely that you will need to change your beginning to fit your ending than the other way around, so spend time on your ending sooner rather than later!
Are there any works in the post-apocalyptic genre with post-apocalyptic librarians? People who worked in the public library and after the Bad Thing decide to stay and keep the library clean, safe and available for anyone who needs it. People can’t remove books from the premises anymore, because they’re too precious, but you can stay as long as you want and read them or copy them out–the librarians encourage making copies, so that the information can circulate beyond the physical boundaries of the library.
After a while it becomes an unspoken reality of the post apocalyptic society that you Just Don’t fuck with the library. You don’t fight there, you don’t steal from it, you don’t allow harm to come to librarians when they have to leave the building for supplies.
People donate food and books and paper with no expectation of reciprocity, because the librarians don’t ask for anything when you need a place to hide or information or, fuck, to read a schlocky crime novel because you need to escape reality in some purple prose.
Reactions
I have a list of topics that I want to get to on this blog. But while I love talking about my feelings on pop culture and the creative process and feminism, this is also a personal blog. So, I’ve been trying to put my thoughts on Baghdad, Beirut, and Paris into words, and it’s left me with a distinct weariness. I’m going to use “we” a lot in this post; mostly, I am referring to the Western…
View On WordPress
-
 aech-posts-stuff liked this · 2 months ago
aech-posts-stuff liked this · 2 months ago -
 sana10 liked this · 5 months ago
sana10 liked this · 5 months ago -
 smokenhagen liked this · 6 months ago
smokenhagen liked this · 6 months ago -
 novembertv reblogged this · 7 months ago
novembertv reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 unclerik77-blog reblogged this · 8 months ago
unclerik77-blog reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 carolichou reblogged this · 9 months ago
carolichou reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 carolichou liked this · 9 months ago
carolichou liked this · 9 months ago -
 erinsmysticalhands liked this · 9 months ago
erinsmysticalhands liked this · 9 months ago -
 breivete liked this · 10 months ago
breivete liked this · 10 months ago -
 brookeinred reblogged this · 10 months ago
brookeinred reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 brookeinred liked this · 10 months ago
brookeinred liked this · 10 months ago -
 bonben liked this · 11 months ago
bonben liked this · 11 months ago -
 mormaximumgoatee865 liked this · 11 months ago
mormaximumgoatee865 liked this · 11 months ago -
 figuringoutlifenstuffs liked this · 11 months ago
figuringoutlifenstuffs liked this · 11 months ago -
 capoeri liked this · 11 months ago
capoeri liked this · 11 months ago -
 capoeri reblogged this · 11 months ago
capoeri reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 vernacular-science liked this · 11 months ago
vernacular-science liked this · 11 months ago -
 kaispeakshermind reblogged this · 11 months ago
kaispeakshermind reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 hairmonster42e reblogged this · 1 year ago
hairmonster42e reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 dairxoxo liked this · 1 year ago
dairxoxo liked this · 1 year ago -
 kayceecruz reblogged this · 1 year ago
kayceecruz reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 skvaderarts liked this · 1 year ago
skvaderarts liked this · 1 year ago -
 bomberstillplaysvideogames liked this · 1 year ago
bomberstillplaysvideogames liked this · 1 year ago -
 queensolace liked this · 1 year ago
queensolace liked this · 1 year ago -
 aniyaanv liked this · 1 year ago
aniyaanv liked this · 1 year ago -
 kingco11x liked this · 1 year ago
kingco11x liked this · 1 year ago -
 stanapmysba liked this · 1 year ago
stanapmysba liked this · 1 year ago -
 chaidownnepho liked this · 1 year ago
chaidownnepho liked this · 1 year ago -
 blushshop liked this · 1 year ago
blushshop liked this · 1 year ago
check out my main blog www.theferalcollection.wordpress.com and find fandoms and funstuff on www.theferalcollection.tumblr.com
103 posts