Valerie00diamond - Untitled

More Posts from Valerie00diamond and Others
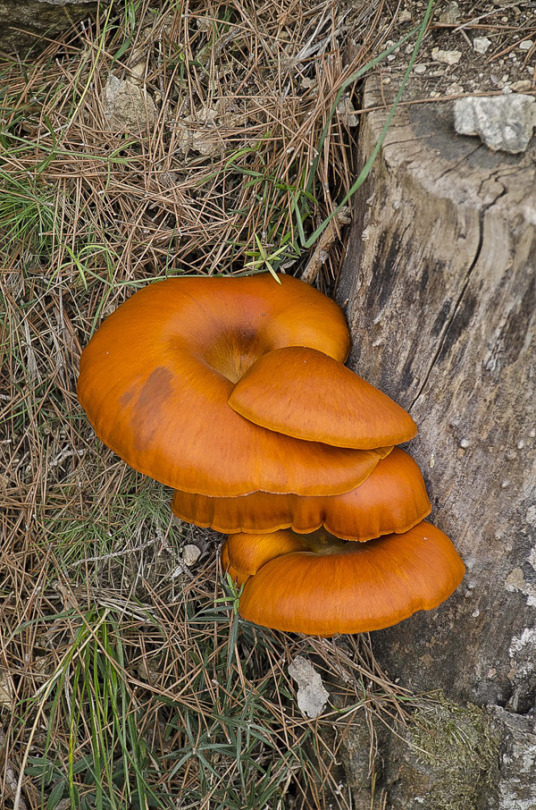
(Don't eat them raw ever even after being dried)
If you see this post please get your own information.Don't want anyone getting sick! or worse!
Black moral


Find:especially under white ash,also under tulip poplars, oak, and hickory.
Time:springtime
Description:Honeycombed cap with black to brownish black ridges and yellowish brown pits; completely hollow. April and early May. Cap elongate and conical, with vertically elongated ridges and pits; ridges are black to brownish black, pits are yellowish brown; texture deeply pitted; hollow; bottom of cap is fused to the stalk. Stalk sometimes enlarged at the base; whitish; texture granular; hollow. Spore print white to cream. Spores magnified are elliptical, smooth. Spores are located inside the pits.
Size:Cap width ½–1½ inches; cap height: ½–2 inches; stalk length: 2–4 inches; stalk width: ½–1½ inches.
Look alikes: The poisonous false morels are reddish and have wrinkled, lobed, or brain-shaped caps and dense (not hollow) stalks. The bottom half of the cap of the half-free morel hangs free from the stalk.


Bear's Head Tooth

Find:grow on dead or dying wood and shaded areas of deciduous and alpine forests.
Time:late summer and autumn months
Description:Edible when young – be sure it is white.Is white when fresh and yellows with age. It has long spines and a branched fruiting body. The fungus is 15-30cm (6-12”) across. It is a tightly branched structure which develops from a rooted base. When young, before the branches have developed.
Look alikes:edible mushroom lion’s mane(on L) does not branch even in maturity.May slow blood clotting.Its spines are long, though not quite as long as those of bear’s head.those who are pregnant or breast feeding should not take Lion's Mane.edible mushroom comb tooth or coral tooth(on R) has a very similar branching structure, but its spines remain very short. It does indeed resemble a branched hard coral, or possibly a small tree branch feathered with hoarfrost.


Golden Chanterelle

Find:They require established woodland to grow.They’re most commonly found around maple, beech, poplar, birch and oak trees. In some areas, they’re associated with pine and fir trees, so it doesn’t have to be hardwood.require moist habitat, and they’re most abundant in wet summers with consistent rain.
Description:Chanterelles have forked ridges on their underside, and the forking is a characteristic of true chanterelle mushrooms.They’re not exactly true gills, and they have blunt edges.The ridges run down the stem of the mushroom, which is another identifier.Yellow to orange in color on outside.Growing as individual mushrooms(not groups) most of the time.Chanterelles always grow on the forest floor, never on wood.Thick, blunt ridges instead of true gills.Forked ridges rather than straight,The flesh inside is a pale creamy white, not orange like the surface.Smells sweet like fruit, like apricots.The cap edge is wavy, thin and irregular.
Look alikes:poisonous look alike Jack-O-Lantern (on L)mushroom is, in fact, an orange mushroom, that’s about where the similarity ends. Jack-O-Lantern mushrooms have true gills, that are not blunt like chanterelle gills. They also don’t fork or run down the stem of the mushroom.Lastly, Jack-O-Lantern mushrooms always grow on wood, often in groups rather than singly.This can be tricky though since the wood they’re growing on may be buried so that it looks like they’re coming out of the forest floor.Apparently, Jack-O-Lantern mushrooms taste quite good, but you still don’t want to eat them.They’re not deadly,but they’ll cause quite a bit of uncomfortable gastric distress.False chanterelles (on R)Deep, thin gills rather than the blunt gills of a chanterelle.Forked gills (like chanterelles)Cap edge is downturned and round.Center of the cap is darker colored, edge is lighter.Smell like a mushroom, not like apricots.




Bear Fishing by Olga Burmistrova
"This is a real photo, not artificial intelligence. Archie is a retired former circus performer. He was born and raised with people. This bear is very inquisitive and loves the attention of the public. "
Delaying the gratification of becoming my full potential has led to poor personal politics; therefore, the thriving of the fascist regime is one I have become complicit to.
Once the harsh winter is gone, when come the good and easier days, we often encounter bears swimming by the ice edge. Polar bears are extremely capable of having fun alone with whatever they find 🐻❄️ !.
Five Timeless Techniques for Mastering Knowledge
1. Spaced Repetition
Steps:
Identify Key Information: Select the material you need to learn.
Create a Study Schedule: Space your study sessions over increasing intervals (e.g., 1 day, 3 days, 1 week, 2 weeks).
Review Regularly: Revisit the material at each scheduled session.
Scientific Basis: Spaced repetition leverages the spacing effect, a phenomenon where information is more easily recalled when study sessions are spaced out over time. Research shows this technique enhances long-term retention compared to cramming.
2. Cornell Method
Steps:
Prepare Your Paper: Divide your paper into three sections: a narrow left column for cues, a larger right column for notes, and a summary section at the bottom.
Take Notes: During lectures or readings, jot down key points in the right column.
Cue Column: After the session, fill in the left column with questions or keywords related to your notes.
Summarize: At the end of your notes, write a brief summary of the main points in the bottom section.
Review: Use the cues to test your recall and understanding.
Scientific Basis: The Cornell Method promotes active engagement with the material and encourages self-testing, which are both linked to improved memory and understanding through the retrieval practice effect.
3. SQ3R Method
Steps:
Survey: Quickly scan the material to get an overview.
Question: Formulate questions based on headings and subheadings.
Read: Read the material carefully to find answers to your questions.
Recite: Summarize the information in your own words.
Review: Go over the material again to reinforce learning.
Scientific Basis: SQ3R is based on principles of active reading and metacognition. By engaging with the material in multiple ways, learners can deepen their understanding and retention.
4. Priming
Steps:
Preview Material: Briefly look over the material before diving into a detailed study session.
Set Goals: Define what you want to achieve with your study session.
Contextual Exposure: Expose yourself to related concepts and ideas in everyday life.
Scientific Basis: Priming relies on the brain's ability to make connections between related pieces of information. It can enhance learning and recall by creating a mental framework that makes new information easier to integrate.
5. Metacognition
Steps:
Plan: Before starting, plan your approach to the study session.
Monitor: Keep track of your understanding and progress during study.
Evaluate: After the session, assess what you've learned and how well you understood it.
Scientific Basis: Metacognition involves thinking about one's own thinking processes. It encourages self-regulation and reflective practices, which research shows can significantly enhance learning outcomes by promoting deeper understanding and strategic use of cognitive resources.
-
 locasimmardiamor liked this · 2 weeks ago
locasimmardiamor liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 mayonaisie liked this · 2 weeks ago
mayonaisie liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 the-mitochondrion liked this · 2 weeks ago
the-mitochondrion liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 thewickerking liked this · 2 weeks ago
thewickerking liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 rubyneo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
rubyneo reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 take-me-whole liked this · 2 weeks ago
take-me-whole liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 rodamned liked this · 2 weeks ago
rodamned liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 alamuts-lair-of-madness reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
alamuts-lair-of-madness reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 alamuts-lair-of-madness liked this · 2 weeks ago
alamuts-lair-of-madness liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 honeybouquets reblogged this · 2 weeks ago
honeybouquets reblogged this · 2 weeks ago -
 fortunaerotaa liked this · 2 weeks ago
fortunaerotaa liked this · 2 weeks ago -
 strongholdinthedark reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
strongholdinthedark reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 perfectlypreservedocs reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
perfectlypreservedocs reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 knight-of-obliveon reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
knight-of-obliveon reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 withdullscssors reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
withdullscssors reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 chibisatou liked this · 3 weeks ago
chibisatou liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 rinzukodas reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
rinzukodas reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 raynshyu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
raynshyu reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
wings-scales-fire reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 about84bears liked this · 3 weeks ago
about84bears liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sharktino reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
sharktino reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 writtenacrossthestars liked this · 3 weeks ago
writtenacrossthestars liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 permissiontogeek liked this · 3 weeks ago
permissiontogeek liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 lsd-se-vraca-kuci2 liked this · 3 weeks ago
lsd-se-vraca-kuci2 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 sharktino liked this · 3 weeks ago
sharktino liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 marshmallowdoritos reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
marshmallowdoritos reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 sshdaemon reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
sshdaemon reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 ianthe-brainrot liked this · 3 weeks ago
ianthe-brainrot liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 you-newer-know-1 liked this · 3 weeks ago
you-newer-know-1 liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 theensomnios reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
theensomnios reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 voxblade reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
voxblade reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 lizzyemily reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
lizzyemily reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 dream-castt reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
dream-castt reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 poison-rot liked this · 3 weeks ago
poison-rot liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 caguaydreams reblogged this · 3 weeks ago
caguaydreams reblogged this · 3 weeks ago -
 caguaydreams liked this · 3 weeks ago
caguaydreams liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 koisokasvi59 reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
koisokasvi59 reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 koisokasvi59 liked this · 4 weeks ago
koisokasvi59 liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 ohhhellnno reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
ohhhellnno reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 ohhhellnno liked this · 4 weeks ago
ohhhellnno liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 suomaahinen reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
suomaahinen reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 suomaahinen liked this · 4 weeks ago
suomaahinen liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 antarctic-arcanine liked this · 4 weeks ago
antarctic-arcanine liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 haertel-comics liked this · 4 weeks ago
haertel-comics liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 fudge-mudge reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
fudge-mudge reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 herr--katze liked this · 4 weeks ago
herr--katze liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 cyberpunkwarlok reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
cyberpunkwarlok reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 terpsikeraunos liked this · 4 weeks ago
terpsikeraunos liked this · 4 weeks ago -
 icaruslorenzo reblogged this · 4 weeks ago
icaruslorenzo reblogged this · 4 weeks ago -
 icaruslorenzo liked this · 4 weeks ago
icaruslorenzo liked this · 4 weeks ago



