Dive Deep into Creativity: Discover, Share, Inspire
Invertebrates - Blog Posts
Hanging out. Thinking about stuff.
OOO WHAT IF I DRAW MD CHARACTERS AS INVERTEBRATES?
What invertebrates MD characters should be you think? I will make them a hybrid freak of nature anyways. However I'm not that nerdy to remember each species name :(
Invertebrate species of MD characters ⬇
Uzi - Giant Africa milli. x Galapagos centi. + Colorado Hairstreak butterfly
Cyn - Amazonian Giant centipede + New Guiana flatworm
N - Vespula wasp + Giant Leopard moth
V - Orchid mantis + Weidemever's Admiral butterfly
J - Indian ornamental tarantula + Meollenkampi Rhino beetle
Lizzy - Peppered moth
Thad - Eastern Tiger Swallowtail butterfly
Doll - Dead Leaf mantis + Cecropia moth
Yeva - Dead Leaf mantis
Yeva's husband (don't remember his name) - Cecropia moth
Nori - Giant African millipede + Galapagos centipede
Khan - Colorado Hairstreak butterfly
Alice - Spiny Flower mantis + Atlas moth
Beau - Arizona Sister butterfly larvae
Sentinels - Giant Wolf x Jumping spiders (no specific species)
will add more characters soon
useless fun fact: when I was a lil kid, I was shitless scared of roaches and wasps and bees, but not spiders??
I, uh, might do that… except I’d probably worry too much about the welfare of the bugs.
Me walking around with a “Free Bugs” T-shirt and when people ask I point out all the little guys around them and tell them which ones are introduced species that they can totally just grab off the street and keep as pets
walking around with a “Free Bugs” tshirt and cargo pants with a lot of very full pockets that are visibly writhing
This. This is what got me into insects and other “bugs” as a small child. I was (and still am) an animal lover and they were the animals that were right there in my backyard and easy enough for a child to catch and play with. They are such cute little creatures 🪲🐜🦋🦗🐛
everyone should try to get into bugs because they fulfill all your primal needs to get Way Too Close to wildlife and hold and pet wild creatures
When you start recognizing bugs as friendly and cute little Guys, your world opens up so much.
They're easy to obtain. Do you want isopods? Just put a piece of cardboard on the ground and you will have isopods. There's a straight-up CLOUD of bees, wasps, butterflies, and flies around my Swamp Milkweed. Planting any native flower will make you so many friends. Better yet, do nothing—any somewhat overgrown area is habitat. I was hacking down some of the grasses in the Weed Area in our back yard yesterday (the non-native chicory is overpopulated and the native perennials are getting swallowed up by a Crap Ton of non-native grass) and found a enormous katydid.
I am feeling such awe and wonder over how tame and unbothered insects are in front of humans. Lots of them you can catch and hold in your hands and they will just be like oop oh well this is strange sorry to bother you and fly away.
They are so beautiful too! The COLORS. Electric blue! Iridescent green! Bright red! Every metallic shade! Rainbow! Our yard is full of dragonflies now and they've got to be one of the world's most elegant creatures.


Yesterday afternoon I dragged my friend to Denge Wood forest. While there, I spotted one of my top five favorite beetles. These lustrous and magnificent little guys are green tiger beetles (Cicindela campestris).
They are incredibly fast predatory beatles that hunt down and eat other insects. The larvae of this beetle live in individual burrows in sandy soil. They flick out the sand around them creating a pitfall that other insects fall into.
So beautiful but deadly.









Some after work Instagram browsing brought up an unexpected gem today as it randomly decided to show me some automatons.
I haven't seen any since childhood, where I vaguely recall them featuring on quirky supernatural or spooky shows as creepy curiosities from time to time.
I hadn't realised that they were still made or indeed that they could be made into such beautiful creations. With serenely swimming whales, cantering horses and fluttering birds & insects.
I decided to see if I could make a basic one using bits and bobs from my room. This ended up including black card, scissors, a bamboo skewer from one of my orchids, wire and wire clippers, a thin cylindrical ice cream stick that I saved from a kulfi, and hot glue and my glue gun.
It took a bit of time to wrap my head around the (admittedly very basic) mechanics and the end result is liable to come apart at the seams if I so much as think about turning the mechanism too vigorously. But I am happy with my first attempt.
If I can figure out how to make a less slap dash mechanism then I might make a realistically painted deaths head hawk moth automaton. I am rearing some caterpillars of this species so I am ever so slightly obsessed with them at the moment. You can see the caterpillars at the top of this post and I don't think I am alone in thinking they are absolutely gorgeous little buggers.




The college I work for has recently got some hives and they kindly paid for me and my colleagues to do an amazing beekeeping course.
This week I did a solo hive inspection for the very first time, as I was the only trained person on site.
It has been a magnificent, if nerve-wracking experience and I can't wait to do it again next week. I am forever petrified of squishing the queen but I will hopefully get more confident with time.
We have one large hive and one smaller one. The large hive is going strong and each week we have to rearrange everything so they don't run out of space. To do this you move empty frames towards the centre of the brood box so the Queen has access to at least 2 empty frames. For some reason she only likes laying eggs on frames near the centre. You also have to check that there's enough space in the supers as this is where worker bee store most of the honey. If the colony doesn't have enough space then the bees start to get agitated and it can prompt a swarm.
The smaller hive unfortunately lost its Queen when it was being delivered to us. So we are currently trying to raise a new one. To do this we moved over a tester frame containing newly laid eggs and some grubs from our other hive. The worker bees then chose the new Queens and built special large cells for them. we knocked down all but one of these to stop a potential swarm. We then left this hive for 3-weeks to give her a chance to emerge and go on her nuptial flight. On this flight she will hopefully have mated with a number of genetically diverse drones. She has around a 30% chance of surviving this and coming back to the hive. We haven't seen her yet but fingers crossed she's there. The workers had started to make play cups indicating that they are dissatisfied with the lack of new eggs being laid. But it does take a while for her to start laying. As we don't know if she survived I put in two new tester frames with eggs and grubs from the other hive. When I do an inspection next week I will need to check for freshly laid eggs and queen cells. If I see new eggs then I know that the Queen survived, but if not and if Queen cells have been produced then we'll have to start the process of raising a Queen again.
The pictures above are from the smaller hive showing some play cups on a couple of the frames. This shows the workers are irritated at the lack of new eggs being laid. One picture also shows the entrance to the hive and one of the worker bees has pollen on their legs. This is apparently an indication that a new queen is present and is about to start laying.
General Bee info:
The Queen has a store of sperm and can control which eggs are fertilised with a little flap. Unfertilized eggs turn into drones (haploid, reproductive males). Fertile eggs turn into either worker bees (usually non reproductive, female bees) or new Queens. She lays individual eggs into each of the cells.
In a healthy hive, drones are only present in the summertime when the hive has reached sexual maturity. In an unhealthy hive the Queen can start laying drone eggs when she runs out of stored sperm. Queenless workers may also start to lay drone eggs.
When the eggs hatch, worker bees feed and nurture the grubbs with honey and variety of different pollen. It is the worker bees that choose what fertile eggs become Queens. The ones they select as potential new Queens are fed a diet of mostly royal jelly and they build larger cells for them. Workers can also choose when new queen's emerge by standing on top of the flap door to their cell. This prevents them from emerging until the workers deem the time is right.
As time progresses grubs get larger and eventually pupate within their cells. The cells are then capped with wax and the pupae starts to metamorphose internally. When the pupa are fully developed they moult and then chew their way through the wax cap. Young bees can be quite light-colored when they first emerge.
Unfortunately I don't have very many pictures of our lovely hives. It is quite hard to take photos with massive gloves on, and the longer you spend faffing around, the more stressed out the bees get. I only got these pictures because I needed to update my colleagues on certain developments. If the opportunity arises again then I will share any photos here as I think bees are really interesting.
My two hand painted lepidoptera hair clips.
Now with a fancy "aesthetic" background as I had some banana leaves handy.





I had to cut some banana leaves down at work yesterday as they were threatening to grow through the greenhouse roof. So I took some pictures before putting the leaves in the avary so the birds could have a nibble.
I made the hair clips out of an old pair of jeans, acrylic paint, hot glue and French barrette hair clips.
I cover the process of making them in a previous post. If you fancy giving it a go, I would love to see what you make.
My last two atlas moths have emerged from their cocoons. They are beautiful and absolutely fascinating.
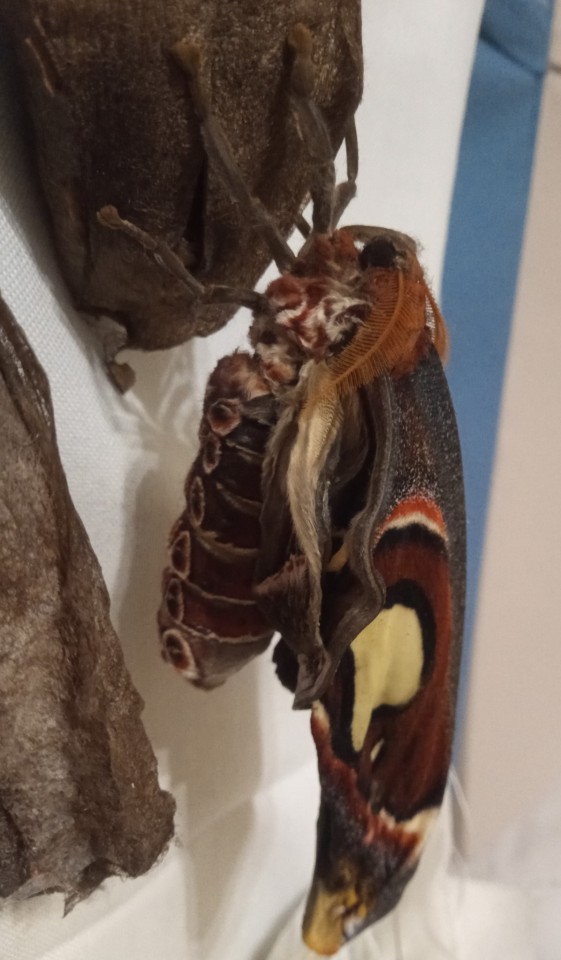





Can you see the snake head markings on the tip of each forewing? They are there to deter potential predators, which I think is pretty neat.
They are absolutely gorgeous, and I am so glad that they have all hatched safely. Unfortunately, I think these two are both female so it looks like I won't be getting any fertile eggs.
One damaged it's hind wing a little when it flew into one of my orchids. It is the only one that has shown any interest in flying and has been having short (approximately 2 min) flights around my room every evening. Finding a new place to lay eggs each time.
I attended an invertebrate show with my friends a few months back and ended up picking up four atlas moth cocoons towards the end.
I wasn't sure if they would emerge successfully but yesterday I found the first one sitting on my wardrobe.



Isn't it beautiful!

If the others hatch out in time then I will hopefully have some fertile eggs. I really want to see the whole life cycle of these amazing things.
I went fossil hunting down at the Warren (in Folkestone, Kent, UK) on Thursday last week. These are some of my favourite finds from the trip (I washed them up at home).


Fossil hunting is great fun. If you live in the UK, and fancy giving it a shot, then there are some really handy websites that you should check out. https://ukfossils.co.uk/ and http://www.discoveringfossils.co.uk/fossil-locations-of-great-britain/
If you don't live in the UK but still want to give it a go then I would recommend looking for local fossil hunting clubs, societies and websites. Failing that you should try to look for areas where sedimentary rocks are being eroded. For instance, cliffs by the sea, rivers, old quarries, etc.
Just make sure you don't trespass or go anywhere too dangerous. For instance, if you are fossil hunting under cliffs at the beach, don't get to close to the cliffs (falling debris and cliffs collapsing) and plan around the tides (you don't want to get cut off).


Basket Star
Gorgonocephalus caputmedusae
The Basket Star is a strange yet elegant creature that lives in the deep ocean. It resembles a flesh white ball with gnarled and swirling branches. It thrives in locations with strong currents. Its numerous arms move slowly and wrap around prey. They are one of my favorite animals from the Echinodermata phylum.
Photo credit
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00227-005-0032-3
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gorgonocephalus

Pram Bug
Phronima sedentaria
The Pram Bug is a deep sea amphipod that is located between 200 to 1000m in the ocean. It has a translucent exoskeleton and can see primarily blue light. It is also is contained in a hollowed out barrel that is used for protection and to house babies. The image above is a female pram bug carrying its young.
Photo Credit:https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/phronima-female-and-young

Marrus orthocanna
Marrus orthocanna is a deep sea siphonophore found at depths between 400m to 2200m. It has a colony of gas-filled zooids on the top used for locomotion. It also has a long, bright orange tentacles on the bottom. Marrus orthocanna are viscous predators and consume small crustceans and copepods.
Photo credit: http://www.arcodiv.org/watercolumn/cnidarian/Marrus_orthocanna.html

Hula Skirt Siphonophore
Physophora hydrostatica
The Hula Skirt Siphonophore a deep sea siphonophore that is found between 700 m to 1000m. It is made of a colony of hundreds tiny zooids. The top portion of the colony holds the swimming bells, which allow the colony to move. The bottom of the siphonophore holds the orange ‘hula skirt,’ which is full of stinging tentacles.
Photo link : https://twitter.com/montereyaq/status/1162068535331311617?lang=da

Crystal Jellyfish
Aequorea victoria
The Crystal Jellyfish is a graceful, transparent jellyfish with long, thin tentacles. It has bioluminescent organs around it bell that produce a bright, green light. It tends to consume small copepods, but it has the ability to swallow other jellyfish half its size. Furthermore, this jelly is used in biological experiments to detect calcium.
Photo credit: https://www.montereybayaquarium.org/animals/animals-a-to-z/crystal-jelly
https://fineartamerica.com/featured/5-aequorea-crystal-jellyfish-with-amphipods-alexander-semenovscience-photo-library.html
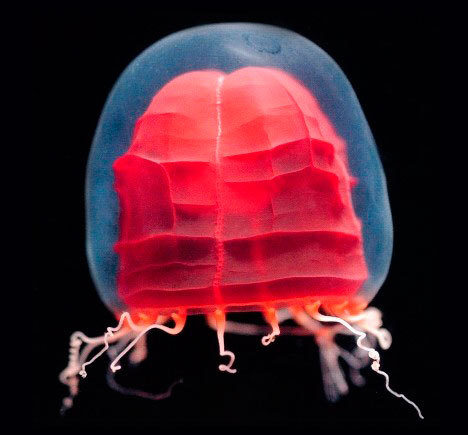

Red Paper Lantern Medusa
Pandea rubra
The Red Paper Lantern resembles a floating, Japanese paper lantern in the deep sea. It has the ability to crumple and wrinkle its bright, red bell, and it is located at depths between 550m to 1200m. It has also been nicknamed the “origami jelly.”
Photo credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Pandea_rubra
http://www.thegorgeousdaily.com/pandea-rubra/

Black Medusa
Vampyrocrossota childressi
The Black Medusa is an inky, black hydrozoan that absorbs all light that hits its tiny body. It has a translucent gelatin and a black umbrella; it is also only 1.5 cm in size. Moreover, it is found at depths between 600m to 1500m, and it spends its entire life floating in the deep ocean.
Photo credit: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/488148047080475827/


Pigbutt worm
Chaetopterus pugaporcinus
The Pigbutt worm or the flying buttocks of the sea is spotted floating between 965 m to 1300 m in the deep ocean. It is actually a polychaete (polly-keet) worm species that burrows in the ground as an adult, and floats around the ocean as a baby. The worm feeds itself : by creating a balloon of mucus; collecting particles on the mucus; and then consuming the particles. It is the rarest and thickest worm in the deep ocean, for only ten have been spotted.
Photocredit: https://roaring.earth/pigbutt-worm/


Jewel Squid
Histioteuthis heteropsis
The Jewel Squid is covered in color-changing photophores that resemble sparkling gem stones. They also have a light-red coloration and are about 20 cm in length. They display a unique behavioral adaptation called diel migration. During the day, they stay at depths around 400-1200 m, and then surface during night (0-400m). This behavioral pattern is designed maximize feeding at night, and avoid predators during the day. The primary predator of the Jewel Squid is the Sperm Whale.
Photo credit: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/722827808920240115/
https://twitter.com/theoctonation/status/1168516522270253056


Pink Helmet
Aglantha digitale
The Pink Helmet is a mini hydromedusa that comes in a variety of vibrant colors. The tiny jelly is only 4 cm in size and is found towards the surface of the ocean. The purple and blue hues we see in its bell are caused by a phenomenon known as iridescence, when light strikes the jelly’s thin tissue at different angles (similar to what we see in a soap bubbles). It also has orange pigmentation near its mouth; this pigmentation helps attract prey and mask luminescence. Furthermore, females tend to be more colorful than males.
Photo credit: https://biolum.eemb.ucsb.edu/organism/pictures/aglantha.html
https://www.pinterest.com/pin/186899453255850798/


Piglet Squid
Helicocranchia pfefferi
The Piglet Squid is a very small and delicate, transparent squid. It is found at depths between 400 to 1000 m. It has an unique siphon that is used for jet propulsion and it resembles a pig muzzle. The young piglet squids tend to live close to the surface, and steadily migrates downward as they grow. This behavior is called ontogenetic migration.
Photo credit: http://photo.cctv.com/2019/07/23/PHOAKMEBh8xJRaHXEUIGx8kE190723.xml
https://www.ourbreathingplanet.com/banded-piglet-squid/

Glass Octopus
Vitreledonella richardi
The Glass Octopus spend its entire life in the midwater section of the ocean and found at depths between 200m to 2000m. Even though it has no protection from predators, it achieves perfect transparency. The only part of the Glass Octopus that is visible is its digestive gland. However, the digestive gland is placed vertically to minimize detection. In addition, I find this octopus to be super cute!
Photo credit: https://www.mynumer.com/forums/topic/499/invisible-animals/view/post_id/859

Black- eyed squid
Gonatus onyx
The Black-eyed Squid is roughly over one foot (35 am) and is found at depths as deep as 2500m. The female Black-eyed Squid works fiercely to protect her babies, by carrying around a patch of egg for six to nine months. When the eggs hatch, 2000 to 3000 babies are released into the ocean. However, this makes her vulnerable to predators.
Photocredit: http://tolweb.org/Gonatus+onyx/19769


Giant Bell Jelly
Scrippsia pacifica
The Giant Belly Jelly has 256 tentacles attached to a gelatinous bell-shaped base. Like most cnidarians, the Giant Belly Jelly uses specialized stinging cells called nematocysts to catch its prey. When fish and other prey swim into its tentacles, the sensory projection on the cnidocyte (cell that holds the nematocysts) is activated. Then the nematocysts and barb are released, hitting the vulnerable prey and releasing a toxin into the prey’s body. The Giant Bell Jelly is found at 400 m in the ocean. It is related to the jellyfish, but it is categorized as a Hydrozoa (similar to the Portuguese- man-o-war)
https://vimeo.com/42551565
Photo Credit: https://www.pinterest.cl/pin/467107792572034837/
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/ivytech-bio1-1/chapter/phylum-cnidaria/

Sea Angel
Cliopsis krohni
The Sea Angel is a tiny snail that is only 4 cm in length and found at depths as deep as 1500 m. Even though it is small, it is a viscous predator. It hunts other midwater snails using a structure called a radula. Unlike other snails, the Sea Angel’s mouth is located on top of its head. It also uses swimming “wings” to propel through the water.
Photo Source: http://seaslugsofhawaii.com/species/Cliopsis-krohni-a.html
Okay, so this is really cool! You have this phenomenon where some plants grow edible appendages to their seeds to entice ants to carry them underground where they can safely sprout. And then you have wasps which lay their eggs on the leaves, stems, and other parts of plants and trigger the growth of galls (swellings) which both feed and protect the wasp larvae until they reach maturity.
The boy who was watching the ants noticed they were taking wasp galls underground, too. Further exploration found that the wasp larvae were unharmed inside the galls; the only thing the ants had eaten were edible appendages similar to those on the seeds they collected. The wasp larvae stayed safe inside the ant nest, feeding on their galls, until it was time to emerge and head back out to the surface.
So it turns out that the edible portions of the galls have the same sorts of fatty acids as the edible parts of the seeds. And those fatty acids are also found in dead insects. Scientists think that the wasps evolved a way to make the galls they created mimic the edible portions of the seeds to get the ants to collect the galls. This isn't the only example of wasps making use of ants as caretakers for their young, but it's a really fascinating example thereof--especially if you consider ants evolved from wasps at least 100 million years ago.





